When it comes to the performance and reliability of your car, the battery plays a crucial role. The car battery voltage is a key factor in ensuring that your vehicle starts and operates smoothly. In this article, we will explore the significance of car battery voltage, the optimal voltage range, factors affecting voltage levels, testing methods, and tips for maintaining the right voltage. So, let’s dive in and understand what voltage should be on a car battery.
Understanding Car Batteries

Before we delve into the specifics of voltage, let’s first grasp the importance of car batteries. A car battery is responsible for powering various electrical components, including the ignition system, lights, radio, and more. Without a properly functioning battery, your car may fail to start or experience electrical issues while on the road.
Components of a Car Battery
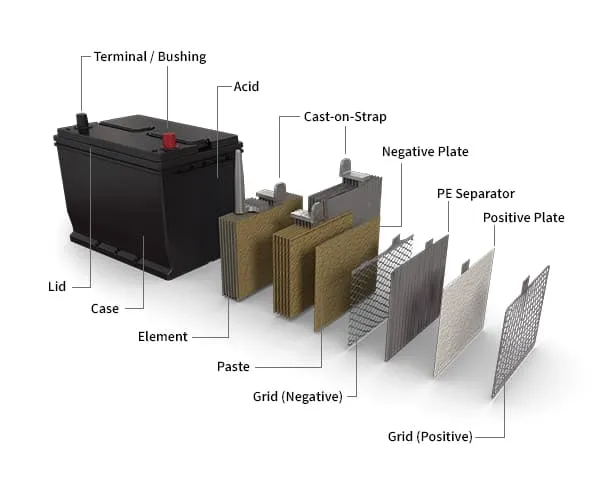
Car batteries consist of several components working together to provide electrical power. These include the positive and negative plates, separators, electrolyte solution, and battery terminals. The chemical reaction between the plates and the electrolyte generates electrical energy, which is then stored and released as needed.
What is Car Battery Voltage?

Voltage is a measure of the electrical potential difference in a circuit. In the case of car batteries, it determines the amount of electrical energy available for starting the engine and powering the vehicle’s electrical systems. Understanding the optimal voltage range is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of your car.
Normal Car Battery Voltage
The ideal car battery voltage range typically falls between 12.4 to 12.7 volts when the engine is off. When the engine is running, the alternator charges the battery and maintains the voltage level between 13.7 to 14.7 volts. These voltage ranges provide the necessary power to start the engine and keep the electrical components running efficiently.
Factors Affecting Car Battery Voltage
Several factors can impact the voltage levels of a car battery. It’s essential to be aware of these factors to prevent any potential issues.
Temperature

Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect the performance of a car battery. High temperatures can cause the battery’s electrolyte to evaporate, leading to reduced voltage. On the other hand, cold temperatures increase the internal resistance of the battery, making it more difficult for the chemical reaction to occur and lowering the voltage output.
Age and Wear

Car batteries have a limited lifespan, typically around 3 to 5 years. As the battery ages, its capacity to hold a charge decreases or it dies, resulting in lower voltage levels. Additionally, wear and tear over time can lead to internal damage or faulty connections, further affecting the battery’s voltage. So full charge car battery voltage is relatively higher than an old car battery voltage.
Charging System Issues
Problems with the car’s charging system, particularly the alternator, can impact the battery’s voltage. If the alternator fails to provide a sufficient charge, the battery may not reach its optimal voltage level, leading to poor performance and potential starting issues.
Parasitic Draws
Certain electrical components in a vehicle, such as alarm systems or aftermarket accessories, can cause parasitic draws on the battery. These draws continue to consume power even when the engine is off, gradually depleting the voltage. Identifying and addressing these draws is crucial for maintaining optimal voltage levels.
Car Battery Voltage Fluctuation While Running
- While a car is running, it is normal to observe voltage fluctuations in the battery due to the charging process.
- The alternator in the vehicle’s charging system is responsible for maintaining the battery’s voltage while the engine is running.
- Under normal operating conditions, the alternator keeps the battery voltage within the optimal range of 13.7 to 14.7 volts.
- These voltage fluctuations help ensure that the battery is being charged effectively and that the electrical components of the vehicle receive sufficient power.
- If you notice significant or irregular voltage fluctuations while your car is running, it is recommended to have the charging system inspected by a qualified mechanic to identify any potential issues.
Testing Car Battery Voltage
To ensure your car battery is operating within the recommended voltage range, periodic voltage checks are necessary. Here are two common methods to measure car battery voltage:
- Multimeter: Use a multimeter set to the DC voltage mode. Connect the positive (red) probe to the battery’s positive terminal and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal. The multimeter will display the voltage reading.
- Battery Load Test: This test measures the battery’s voltage under load conditions. It provides a more accurate assessment of the battery’s capacity to deliver power. You can perform this test using a specialized battery load tester.
Read More: How to Connect a Car Battery?
Ideal Voltage Readings
When conducting a fully charged car battery voltage test, the readings should fall within the optimal ranges mentioned earlier. If the battery voltage is consistently below 12.4 volts when the engine is off, or above 14.7 volts when the engine is running, it may indicate a problem that requires attention.
Maintaining Optimal Voltage Levels
To ensure your car battery maintains the proper voltage levels, consider the following tips:
Regular Battery Checks: Make it a habit to check your battery’s voltage regularly, especially before long trips or during extreme weather conditions. This will help you identify any voltage-related issues early on.
Proper Charging Techniques: If your battery voltage is consistently low, you may need to charge it. Use a quality battery charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure a proper charge. Avoid overcharging, as it can lead to damage.
Avoiding Deep Discharges: Deeply discharging your battery regularly can significantly impact its overall lifespan and voltage levels. Whenever possible, avoid running electrical components while the engine is off and minimize excessive idling.
Troubleshooting Voltage Problems
If you experience voltage-related issues with your car battery, it’s essential to troubleshoot and address the problems promptly. Here are some common symptoms and their potential causes:
Low Voltage Symptoms
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Dimming or flickering lights
- Slow or weak electrical system response
High Voltage Symptoms
- Overcharging of the battery
- Excessive electrolyte loss
- Damage to electronic components
Car Battery Voltage Chart
Here’s a car battery voltage chart:
| Battery Voltage | State of Charge |
| 12.7V – 12.6V | 100% – 75% |
| 12.5V – 12.4V | 75% – 50% |
| 12.3V – 12.2V | 50% – 25% |
| 12.1V – 12.0V | 25% – 0% |
| Below 12.0V | Discharged |
Please note that this Car Battery voltage Chart is general guideline and may vary slightly depending on the battery type and manufacturer. It’s always recommended to refer to your specific battery’s user manual for accurate information on voltage levels and state of charge.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining the right voltage on your car battery is crucial for optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the ideal voltage range, testing methods, and factors affecting voltage levels will help you keep your battery in top condition. Regular checks, proper charging techniques, and preventive measures against voltage-related problems will ensure a longer lifespan for your car battery.
FAQs
How often should I check my car battery voltage?
It is recommended to check your car battery voltage at least once every three months or before long trips. Regular checks can help identify any potential voltage-related issues early on.
Can a car battery die suddenly due to low voltage?
While low voltage can affect the performance of a car battery, a sudden and complete battery failure is usually caused by other factors, such as a faulty cell or a depleted charge.
What should I do if my car battery voltage is too high?
If your car battery voltage consistently exceeds the recommended range, it may indicate a problem with the charging system. It is advisable to have your vehicle inspected by a professional mechanic to diagnose and rectify the issue.
How does cold weather affect car battery voltage?
Cold weather increases the internal resistance of a car battery, making it more challenging for the chemical reaction to occur. This results in reduced voltage output and can impact the battery’s overall performance.
Is 14.5 volts good for a car battery?
Yes, 14.5 volts is considered a good voltage for a car battery when the engine is running. This voltage level indicates that the battery is receiving an optimal charge from the alternator.
What should be the car battery charging voltage?
The typical charging voltage for a car battery is between 13.7 to 14.7 volts.
This voltage range ensures that the battery receives a proper charge from the alternator, maintaining its performance and capacity.
